Personal advice anonymously in our GummiLove Sexpert chat or in person at a Specialist centre in your canton is always a good idea.
Emergency contraception
Emergency contraceptionAnother term for the morning-after pill. prevents unwanted pregnancyPregnancy is the time between the fusion of sperm and egg and the birth of the baby, which normally lasts around 9 months. The first sign of pregnancy is the absence of menstrual bleeding, which would otherwise occur regularly. after inadequate or unprotected sexual intercourseIt is a technical term for "having sex" and specifically means when a penis penetrates a vagina or a vagina receives a penis. It refers to a sexual encounter between two or more people. In colloquial language, there are various expressions .... It should be taken within 48 hours and at the latest 120 hours after sexual intercourse. The sooner, the better the effect. In Switzerland, emergency contraceptionDamit ist die Verhinderung, resp. Verhütung einer Schwangerschaft gemeint. Dazu stehen viele verschiedene Methoden und Verhütungsmittel zu Verfügung. Die meisten stehen aber leider nur Menschen zur Verfügung, die auch schwanger werden k... is available over the counter in all pharmacies. Emergency contraceptionContraceptives are measures that can help to prevent unwanted pregnancies. Most contraceptives must be taken by girls or people with a uterus. Depending on the product, safety is more or less guaranteed. No method is 100% safe. is not a contraceptive method and is therefore not intended for regular use.
It is for women (and anyone else with a uterusObsolete word for uterus) in the following emergency situations:
- Unprotected intercourse
- Tearing or slipping of the condomAuch Präservativ genannt. Ein Kondom ist eine schlauchförmige Gummihülle, die über den Penis gestreift wird, um während des Geschlechtsverkehrs eine Barriere zu bilden und so eine Schwangerschaft und/oder die Übertragung von sexuell ...
- Forgetting the pillThe pill (see contraceptive pill) is a hormonal contraceptive to prevent pregnancy. The hormones taken daily with the pill have the following effects: 1. no ovulation takes place and therefore no egg is available for fertilization, 2. the l... by more than 12 hours
- Vomiting or diarrhea after taking the pill
- Contraceptive failure of NuvaRing or hormoneHormones are chemical messengers produced in the body that control various bodily functions. They are produced by certain organs and transported through the blood to influence the cells and tissues in the body. They influence things such as...
1. pregnancy prevention concerns everyone involved in sex that could result in a child.
Contraception not only concerns people who can become pregnant (e.g. cisCis is a term used to refer to people whose gender identity matches the gender they were assigned at birth. For example, if someone was born male and identifies as male, they would be referred to as a cisgender man. In contrast, someone who... women), but also anyone who can contribute to a pregnancy (e.g. cis men). Everyone involved is responsible for their sexuality and the consequences of their actions. Contraception is important to avoid unwanted pregnanciesPregnancy is the time between the fusion of sperm and egg and the birth of the baby, which normally lasts around 9 months. The first sign of pregnancy is the absence of menstrual bleeding, which would otherwise occur regularly. (and STIsSTI is the abbreviation for "sexually transmitted infections". Sometimes only the abbreviation STI is used in specialist circles or in brochures.). It is also important that everyone involved takes responsibility for contraception in order to have an equal and respectful relationshipA relationship is a deep, close connection between two or more people. Relationships can be romantic, platonic, sexual or familial and can take various forms, such as couple relationships, friendships or parent-child relationships. Maintain....
5 facts why better with a condom 🙂
2. the vast majority of contraceptive methods are for people who can get pregnant
There are six different types of contraception that people with a uterus (e.g. cis women) can use:
HormonalHormones are chemical messengers produced in the body that control various bodily functions. They are produced by certain organs and transported through the blood to influence the cells and tissues in the body. They influence things such as... methods: These include the pill, the contraceptive patch, the vaginal ringThe contraceptive ring, also known as the vaginal ring, is a widely used form of contraception. The ring, which is made of soft, stretchy plastic, is inserted directly into the vagina and releases hormonal contraceptives over a certain peri... and the contraceptive stick. These methods use hormonesHormones are chemical messengers produced in the body that control various bodily functions. They are produced by certain organs and transported through the blood to influence the cells and tissues in the body. They influence things such as... to suppress ovulationOvary is the medical term for a woman's ovaries. Ovulation refers to the process of ovulation in which an egg "jumps" from a follicle in the ovaries into the fallopian tube. and change the thickness of the cervical mucus to prevent pregnancy.
Barrier methods: These include so-called female condomsAnother word for femidom. (femidomThe femidom is also known as the female condom. It is a tube made of thin, tear-resistant plastic (polyethylene or polyurethane) that is inserted into the vagina before sexual intercourse and adapts to the inner wall of the vagina. This pre...), the diaphragmThe diaphragm is a contraceptive. It is a kind of soft rubber cup that is inserted into the vagina to block sperm from reaching the cervix. Together with a sperm-killing cream or gel, e.g. made from citric acid, it can effectively prevent p... and cervical cap. They form a barrier and prevent sperm from entering the uterus.
Intrauterine contraceptive methods: These include all systems and devices that are inserted into the uterus. There are various forms, IUDs, chains and many more. These can be hormone-free, e.g. made of copper or gold. However, there are also hormone IUDs that release hormones locally.
Chemical methods: There are chemicals that kill the sperm. So called. SpermicidesSpermicides are substances that kill spermSpermare small, floating cells that are produced in the testicles (more precisely in the seminiferous tubules). They make up part of the sperm. For a baby to be born, a sperm must fuse with an egg c.... No spermicides are currently approved in Switzerland. In the past, they were used in combination with the diaphragm. There are natural spermicides, e.g. made from lemon, which are available in some pharmacies.
Surgical method: This includes sterilizationSterilization is a medical procedure in which a person is surgically altered so that they can no longer have children. Also called a vasectomy. It is a very safe type of contraception and is considered irreversible. This means that it can n.... The fallopian tubes are separated and sutured. These methods are permanent and permanently prevent pregnancy.
Natural contraceptive methods: These include the symptothermal method, the so-called calendar method or the temperature methodThe temperature method is a procedure that is used to determine ovulation and track the cycle. It is based on the observation of daily body temperature changes that typically occur during ovulation. By tracking temperature changes, you can .... With all these methods, the fertileThis refers to the ability to procreate. In other words, the ability to father a child. and infertileAnother word for infertility. daysAnother description for period, menstruation, menstrual or monthly bleeding. are determined to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
3. but there are also contraceptive methods for men and people with sperm
Most people only know about condomsAnother term for condom (also called Parisian or rubber). and vasectomyVasectomy is a medical procedure in which the sperm ducts are cut. This prevents sperm from being expelled during orgasm so that there is no pregnancy. A vasectomy is considered irreversible. This means that it cannot be reversed. for people with sperm (e.g. cis men).
There are other methods, but they are much less well known and unfortunately not freely available on the market. Not yet. There are many projects that are very promising and will hopefully come onto the market in the next few years.
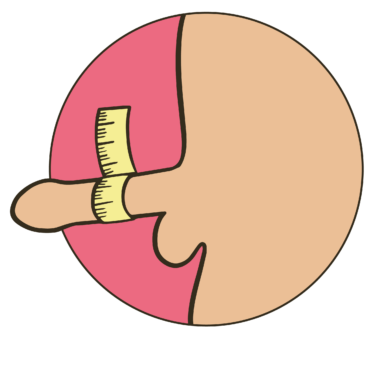
The thermal method, for example, is already available today. It works according to a simple principle: sperm production, known as spermatogenesis, takes place at exactly 34.5 °C. As the body temperature is around 36.5 °C, the testiclesThe testicles are the male gonads in which sperm are produced. This production begins at puberty and continues until the end of life if the glands are intact. There are two testicles in the scrotum below the penis. One testicle is about the... are located outside the body. With the help of a silicone ring, for example, the testicles can be kept in the abdomen so that the testicles are 2 °C too warm and then stop producing sperm.
Our sex expert Jannik explains exactly how this works in the following Watson interview:
You can find outOuting, outing: To out someone is to disclose a person's gender identity and/or sexual orientation to another person or group against his/her will. what other exciting methods there are or could be in the SRF impact article:
4. take your time and find out about the different methods.
There are several ways to find out about different contraceptive methods:
Talk to a (medical) specialist
e.g. gynecologist, sex educator, specialist from a counseling centerThis is a facility where you can get advice from specialists on questions and problems. A visit to an advice center is usually free of charge. As a rule, it is better to call in advance to make an appointment. The specialists at such center....
Find out more on reputable websites
In addition to GummiLove, there are many other good websites where you can find out about different contraceptive methods:
- https://www.sexuelle-gesundheit.ch/themen/verhuetung
- https://www.lilli.ch/schwangerschaft_verhuetung
- https://www.profamilia.de/themen/verhuetung
- https://www.frauenaerzte-im-netz.de/familienplanung-verhuetung/
- https://www.familienplanung.de/
It is important to take enough time to find out about the different contraceptive methods and to obtain information from several sources in order to make a good decision. It is also important to be aware of the possible risks and side effects of the various methods so that you can make an informed decision.
5 Hormonal contraception carries certain risks.
Hormonal contraception carries some risks that can vary from person to person. Some of the possible risks are
- Blood clots (thrombosis): Hormonal contraceptives can increase the risk of blood clots, especially in people who smoke or are overweight.
- Cardiovascular disease: Some studies have shown that the risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack or stroke, may be increased in people who use hormonal contraceptives.
- BreastThe two female breasts together are usually called bosoms. cancer: Some studies have shown that the risk of breast cancer may be slightly higher in people who use hormonal contraceptives.
- Depression and other mental illnesses: Some women may suffer from depression or other mental illnesses when taking hormonal contraceptives.
- Nausea, weight gain, skin changes, headaches, etc.
Discuss your specific situation with a specialist and find out about these and other risks.
6 Not all methods are suitable for teenagers and young adults.
There are some methods that are not recommended for teenagers to use.
The IUDMedical term and collective term for all contraceptive methods that are inserted into the uterus. Also known colloquially as the IUD. and the chain, for example, are not suitable for girls under 16. For people over 16 who have not yet given birthAnother word for the birth of a child., it may be more difficult to insert the IUD or chain. In addition, the gynecologist must use ultrasound to check whether the uterus is already large enough.
Sterilization: Sterilization is a permanent method and is considered non-recoverable (although it is possible in many cases). This method is not available to anyone under the age of 18. As a rule, it will also be very difficult to find a gynecologist who will perform this procedure before the age of 30.
Many experts also advise young people against natural contraception. Firstly, the menstrual cycleCycle is a term used to describe a recurring series of events or phases. It often refers to the menstrual cycle. It refers to the time from the first day of menstruation (period) to the last day before the next menstrual period. This period... is still too irregular to get reliable results and secondly, the method requires a lot of discipline and a regular daily routine, which is not the case for most teenagers. To make a blanket statement about all teenagers is discriminatory and simply wrong. You should discuss with a specialist whether the natural contraceptive method is suitable for you.
Discover in our GummiLove Quickie Podcast 🎙️
An exciting discussion about safer sexSafer Sex ist Sex bei dem geeignete Massnahmen ergriffen werden, um ungewollte Schwangerschaft und/oder sexuell übertragbare Infektionen (STIs) zu vermeiden. Dazu gehört beispielsweise das Verwenden von Kondomen, Lecktücher und Latexhand...! Moni and Alina, accompanied by sex expert Corinne, delve deep into the world of proper contraception. Learn how to talk sensitively with your partner about this important topic. A must for anyone who values responsibility and respect in intimateIntimacy is the feeling of closeness and familiarity that comes from spending time with someone. It can refer to many types of relationships, including romantic, sexual and platonic relationships. It can refer to physical closeness, emotion... relationshipsA relationship is a deep, close connection between two or more people. Relationships can be romantic, platonic, sexual or familial and can take various forms, such as couple relationships, friendships or parent-child relationships. Maintain...!
Want to know more about individual contraceptive methods?
Then take a look here, where you will find fact sheets on each individual infectionHaving an infection or being infected means that you have contracted a pathogen. This can be a flu, herpes or HI virus, for example..
Test your knowledge of contraception now
Take the quiz and find out how much you already know about contraception.
Seximnetz
Questions about contraception
We have received many questions on this topic. The answers from our sex experts are sure to help you too.